A former member of the US Air Force lost both legs after a routine gallbladder surgery and was medically retired. During the surgery, his aorta was lacerated. Subsequent delays meant his legs were without blood flow for hours.
After the damage to the aortic laceration was repaired, still more time passed before the patient was transferred to a civilian hospital for treatment. The Air Force Medical Center did not have a vascular surgeon on-site. By the time the legs were removed, the patient had lost more than 2/3 of his blood volume.
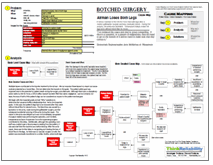 Multiple issues contributed to the injuries received by the airman. We can examine these issues in a visual root cause analysis presented as a Cause Map. First we determine the impacts to the goals. The patient safety goal was impacted due to the potential for patient death during the surgery and aftermath. Although there was no disciplinary action taken by the Air Force, a $54.8 million lawsuit has been filed that claims negligence. Last but certainly not least, the loss of both of the patient’s legs can be considered an impact to the patient services goal.
Multiple issues contributed to the injuries received by the airman. We can examine these issues in a visual root cause analysis presented as a Cause Map. First we determine the impacts to the goals. The patient safety goal was impacted due to the potential for patient death during the surgery and aftermath. Although there was no disciplinary action taken by the Air Force, a $54.8 million lawsuit has been filed that claims negligence. Last but certainly not least, the loss of both of the patient’s legs can be considered an impact to the patient services goal.
We begin with the impacted goals and ask “Why” questions to determine the cause-and-effect relationships that led to the impacted goals. In this case, the patient’s legs had to be removed after they were without blood flow for several hours. The blood loss was caused by a laceration to the aorta, made during the gallbladder surgery, and the subsequent accidental suturing of the aorta during the repair. The repair to the aorta was delayed as it was not immediately recognized. A surgical resident was performing the operation, and it is likely inexperience and lack of supervisor from the supervising surgeon contributed to this delay. Additionally, although the operating room staff was unable to get a blood pressure reading from the patient, it was assumed that the machine was malfunctioning. After the aorta repair, there was further delay in recognizing and treating the loss of blood flow to the legs. As there was no vascular surgeon on-site, the patient was eventually transferred to a civilian facility, where both legs were amputated.
The facility has not commented on the case and so it is unclear what actions might be taken to protect patients. There have been several charges of negligence at the facility in recent years.
To view the Outline and Cause Map, please click “Download PDF” above. Or click here to read more.
